The Transformation of Talent Acquisition in the Age of Artificial Intelligence
The architecture of modern recruitment has undergone a seismic shift, fundamentally altering the relationship between job seekers and potential employers. In the pre-digital era, the resume was a static document, a biography of professional history reviewed by human eyes. Today, it is a data packet, a structured query language intended to be parsed, indexed, and ranked by complex algorithms known as Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) before it ever reaches a human decision-maker. This evolution has created a "digital gatekeeper" effect, where approximately 75% of resumes are rejected by software filters without human intervention, often due to formatting errors or keyword mismatches rather than a lack of qualification.
The introduction of Generative AI, specifically Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, has provided candidates with a potent counter-measure. By leveraging the semantic processing capabilities of AI, job seekers can now analyze job descriptions (JDs) and tailor their resumes with a speed and precision that was previously impossible. However, this technological empowerment comes with significant caveats. While ChatGPT excels at generating text, it lacks the inherent understanding of the rigid, rule-based logic that governs ATS architecture. It is a creative engine trying to operate within a compliance framework.
This report provides an exhaustive, technical analysis of how to utilize ChatGPT for resume tailoring. It deconstructs the process into granular steps, explores the theoretical underpinnings of prompt engineering for career documentation, and highlights the critical limitations of generalist AI. Finally, it presents a comparative analysis of specialized solutions, specifically Reztune, examining how purpose-built applications bridge the gap between AI-driven content generation and ATS-compliant structural integrity.

The "Arms Race" of Recruitment Technology
The recruitment landscape has effectively become an algorithmic arms race. On one side, companies deploy increasingly sophisticated ATS platforms (such as Workday, Taleo, Greenhouse, and iCIMS) to manage the deluge of applications, utilizing semantic search and keyword density analysis to filter candidates. On the other side, candidates are deploying LLMs to mass-produce applications, optimizing their profiles to maximize hit rates.
This dynamic creates a complex environment where the quality of the resume is no longer defined solely by the candidate's actual experience, but by their ability to translate that experience into a format and lexicon that the machine understands. The challenge is twofold: one must satisfy the robotic requirements of the ATS while simultaneously engaging the psychological triggers of the human recruiter who - if the candidate is lucky - will eventually read the document.
The Role of ChatGPT: Tool vs. Solution
It is critical to distinguish between ChatGPT as a tool and a solution. As a tool, ChatGPT is an unparalleled semantic engine. It can rephrase passive sentences into active achievements, synthesize complex job descriptions into core competencies, and identify keyword gaps. However, it is not a solution for the entire application process. It operates on probabilistic text generation, not factual verification or structural design. It can hallucinate skills, misinterpret dates, and generate formatting that looks aesthetically pleasing to a human but is illegible to a parser.
Therefore, the effective use of ChatGPT requires a "human-in-the-loop" methodology - a rigorous process of preparation, prompting, verification, and formatting. This report outlines that methodology in detail.
The Technical Architecture of Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS)
To effectively tailor a resume using AI, one must first understand the adversary. The ATS is not a monolith; it is a category of software that utilizes varied parsing technologies, ranging from simple keyword matching to advanced semantic analysis. Understanding how these systems "read" a resume is the prerequisite for effective prompting.
The Mechanics of Parsing
When a resume is uploaded to an ATS, it undergoes a process called parsing. The system strips away the visual layer of the document - fonts, colors, layout - and attempts to extract the raw data into a structured digital profile.
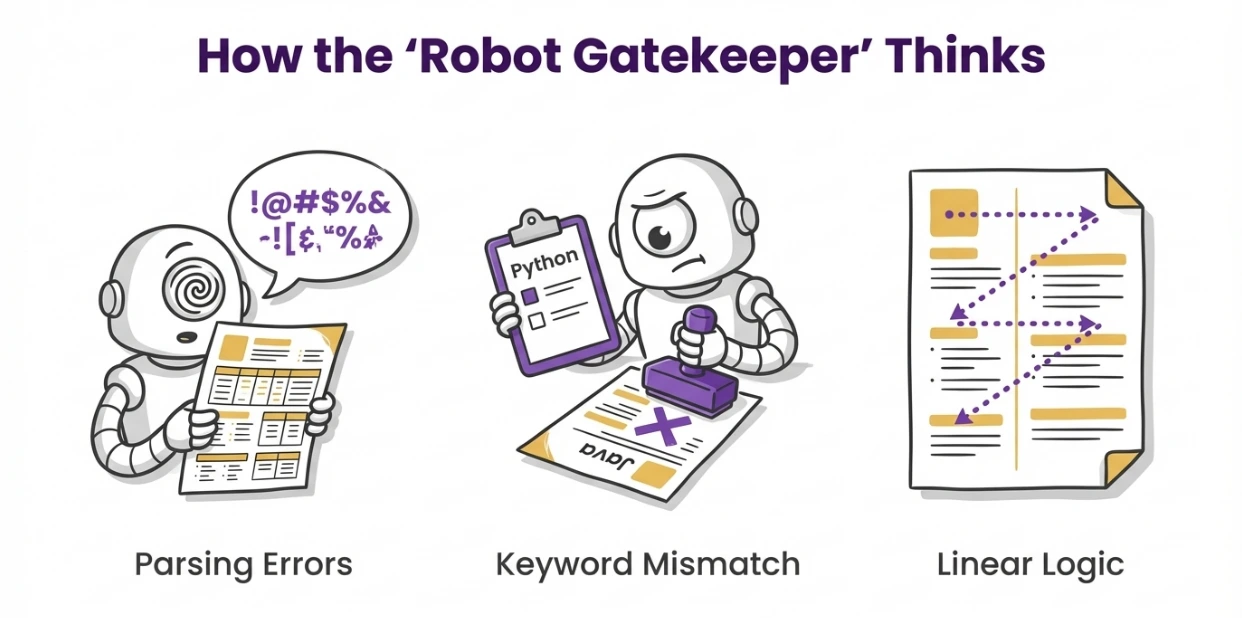
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) vs. Text Extraction: Modern ATSs extract text directly from the file layer. If the text is trapped in an image, a complex table, or a graphic, the parser may fail to read it. This is why "creative" resumes often fail; the parser sees a blank page or garbled characters.
- Entity Extraction: The algorithm scans the text for specific entities: "Job Titles," "Dates of Employment," "Company Names," and "Skills." It relies on standard headings and predictable formatting to identify where one section ends and another begins. If a resume uses non-standard headings like "My Professional Journey" instead of "Experience," the parser may miscategorize the entire section.
- The Left-to-Right Reading Logic: Most parsers read documents linearly, from left to right, top to bottom. Multi-column layouts pose a significant risk. A parser might read the first line of the left column (e.g., "Project Manager") and immediately read the first line of the right column (e.g., "Python SQL"), combining them into a nonsensical string ("Project Manager Python SQL"). This corrupts the data entry, leading to automatic rejection.
Semantic Search and Keyword Ranking
Once parsed, the resume is indexed. Recruiters then search this database using Boolean strings (e.g., "Sales Manager" AND "SaaS" AND "New York"). The ATS ranks candidates based on the frequency and context of these keywords.
- Contextual Relevance: Sophisticated systems (like Rezi or Teal) don't just count keywords; they look for context. They value "Java" more highly if it appears under "Work Experience" in a recent role than if it appears only in a "Skills" list from ten years ago.
- Implicit vs. Explicit Skills: ATS algorithms are increasingly capable of inferring skills. However, explicit matches are still the safest bet. If the JD asks for "Adobe Creative Suite" and the resume lists "Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign," a basic keyword matcher might miss the connection. AI tailoring ensures both the specific tools and the umbrella terms are present.
The Formatting Paradox
Herein lies the central conflict of using ChatGPT. Users often ask ChatGPT to "make my resume look professional." ChatGPT, trained on web data, might generate a resume using Markdown tables or code blocks to organize the text visually. While this looks organized on a screen, tables are kryptonite to many ATS parsers. The complex underlying code of a table can cause the text within it to become invisible or jumbled during extraction.
Strategic Implication: The output from ChatGPT must be treated as raw content only. It must never be used as the final structural template. The content must be migrated to a clean, single-column Word document or a specialized tool like Reztune that guarantees parsing integrity.
Strategic Preparation: The "Master Resume" Protocol
The most common error candidates make is trying to tailor their existing, concise resume directly. This leads to a Frankenstein document - a patchwork of old and new text. The correct approach, advocated by career experts and supported by AI capabilities, is the creation of a "Master Resume" or "Ugly Resume".
Constructing the Master Repository
The Master Resume is a comprehensive, unformatted document that contains everything. It is not meant to be seen by an employer; it is the source code for the AI.
- Data Density: Include every role, every project, every tool used, every metric achieved, and every soft skill demonstrated. Do not worry about length; a 10-page Master Resume is acceptable.
- Granularity: Instead of writing "Managed a budget," write "Managed a $500,000 annual marketing budget, allocating funds across Google Ads, LinkedIn, and OOH campaigns." This level of detail allows ChatGPT to extract specific metrics when needed.
- The "Ugly" Philosophy: By keeping this document unformatted (plain text), you remove the temptation to worry about layout, allowing the focus to remain entirely on data capture. This text-heavy format is also the ideal input for an LLM.
The Semantic Deconstruction of the Job Description (JD)
Before writing a single word of the new resume, the candidate must understand the "question" the employer is asking. The JD is that question. However, JDs are often poorly written, filled with jargon, or vague. AI can be used to decode the JD and extract the hidden requirements.
The Categorization Strategy:
Simply asking for keywords is insufficient. The prompt must force the AI to categorize keywords into logical buckets that map to resume sections: Hard Skills, Soft Skills, and Domain Knowledge.
| Category | Definition | Examples | Resume Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Skills | Quantifiable, teachable abilities. | Python, GAAP, SEO, Forklift Operation. | Skills Section, Bullet Points. |
| Soft Skills | Interpersonal and behavioral traits. | Leadership, Communication, Adaptability. | Summary, Bullet Points (Contextualized). |
| Domain Keywords | Industry-specific terminology. | B2B SaaS, HIPAA Compliance, Agile Methodology. | Summary, Experience Headers. |
| Tools & Tech | Specific software or hardware. | Salesforce, JIRA, Excel (VLOOKUP), AWS. | Technical Skills Section. |
Prompt for JD Deconstruction:
"Analyze the following job description. Extract the top keywords and phrases that are critical for an ATS match. Categorize them into 'Technical Skills,' 'Soft Skills,' and 'Industry Terminology.' Additionally, identify the top 'Pain Points' or challenges this role is hired to solve. Output the data in a structured list."
This prompt does two things:
- Keyword Extraction: It gives the candidate the exact vocabulary to use.
- Pain Point Analysis: It helps the candidate frame their experience not just as a list of duties, but as a solution to the company's specific problems.
Advanced Prompt Engineering for Career Documentation
Prompt engineering is the art of communicating with the AI to elicit the highest quality output. For resume writing, a generic prompt like "Write me a resume" will result in a generic, hallucinated, and ineffective document. To achieve professional results, one must use structured, multi-step prompting techniques.
The Persona-Context-Task-Constraint (PCTC) Framework
To transform ChatGPT from a chatbot into a professional resume writer, the user must establish the framework.
- Persona: Tell the AI who it is. "Act as a Senior Recruiter with years of experience in the." This sets the tone and vocabulary.
- Context: Provide the background. "I am transitioning from Marketing to Product Management. I have the Master Resume attached."
- Task: Define the specific output. "Rewrite my professional summary to target the attached JD."
- Constraints: Set the boundaries. "Do not use buzzwords like 'synergy.' Keep it under sentences. Use active voice only.".
The Iterative Refinement Loop
AI output is rarely perfect on the first draft. The user must treat the AI as a junior copywriter who needs feedback.
- Critique the Output: "This is too generic. Make it more metric-driven."
- Fact-Checking: "You added a skill I don't have. Remove 'Javascript' and replace it with 'HTML'."
- Tone Adjustment: "This sounds too robotic. Rewrite it to sound more natural and professional.".
Step-by-Step Execution: The Professional Summary
The Professional Summary (formerly the "Objective") is the elevator pitch. It sits at the top of the resume and is often the only thing a recruiter reads during the initial 6-second scan. It must be densely packed with keywords and value propositions tailored specifically to the target role.
The "Hook" Strategy
A generic summary ("Hardworking professional looking for a challenge") is a wasted opportunity. A tailored summary ("PMP-certified Project Manager with years of experience leading $5M+ construction projects...") immediately anchors the candidate's relevance.
ChatGPT Workflow for Summaries
Step 1: Input the Variables.
Feed the AI the target job title, the company name (optional but recommended for tailoring), and the top keywords identified in the preparation phase.
Step 2: The Prompt.
"Write a professional summary for a position. I have [Number] years of experience in [Current Field]. Synthesize my experience from the attached Master Resume to align with the following Job Description.
Requirements:
- Start with a strong 'Hook' stating my years of experience and key value proposition.
- Integrate the top keywords from the JD naturally.
- Highlight one major achievement (with metrics) that solves a key pain point in the JD.
- Keep it to 3-4 lines maximum.
- Do not use pronouns like 'I' or 'Me' (use implied first person)."
Step 3: The Pivot Variation (for Career Changers).
If the candidate is pivoting, the prompt must focus on transferable skills.
"I am pivoting from [Old Industry] to [New Industry]. Rewrite my summary to frame my past experience in as a transferable asset for. Emphasize my adaptability and fast learning curve.".
Insight: The summary is the metadata tag for the human reader. While the ATS scans the whole document, the human recruiter uses the summary to decide if the rest of the document is worth reading. An AI-optimized summary bridges this gap by satisfying the algorithm with keywords and the human with a compelling narrative.
Step-by-Step Execution: Work Experience & The STAR Method
The "Work Experience" section is the engine room of the resume. This is where the candidate proves they can do the job. The most critical failure in this section is listing responsibilities instead of achievements. Responsibilities describe what the candidate was supposed to do; achievements describe what they actually did.
The Psychological Power of the STAR Method
The STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) is the gold standard for structuring resume bullet points. It transforms a static duty into a dynamic story of problem-solving.
- Situation/Task: What was the problem?
- Action: What did you specifically do?
- Result: What was the outcome? (Preferably quantified).
ChatGPT is exceptionally skilled at converting raw notes into STAR format, provided it is given the correct prompt structure.
The "Bullet Point Quantifier" Workflow
Step 1: Paste the "Ugly" Bullet.
Take a bland bullet from the Master Resume, e.g., "Responsible for customer service."
Step 2: The Prompt.
"Transform the following resume bullet point using the STAR method.
Original Bullet: 'Responsible for customer service.'
Context: I worked at a high-volume call center, handled about calls a day, and had the highest satisfaction rating on the team.
Instruction: Rewrite this into a single, punchy bullet point. Start with a strong action verb. Quantify the results. The structure should be 'Action + Context + Result'. Use numbers like percentages or dollar amounts if possible (use placeholders like [X]% if you need me to fill in the exact number)."
Step 3: Keyword Injection.
Once the bullets are strong, use AI to inject JD-specific vocabulary.
"Review the bullet points for my role at [Company]. Rewrite them to specifically highlight my experience with, ensuring the terminology matches the JD exactly. For example, change 'managed people' to 'cross-functional leadership' if appropriate.".
Quantifying the Unquantifiable
Candidates often struggle to quantify roles that aren't sales-driven. ChatGPT can suggest proxy metrics.
- Prompt: "I worked as a teacher. How can I quantify my experience? Suggest potential metrics I might not have thought of (e.g., class size, pass rates, curriculum development time).".
- Insight: AI helps candidates uncover hidden data in their own careers, translating qualitative effort into quantitative impact - a language ATS and executives both understand.
Step-by-Step Execution: Skills & Technical Competencies
The Skills section serves as a direct index for the ATS. It allows the parser to quickly categorize the candidate's proficiency. This section requires precision; synonyms are not always recognized by older systems.
Taxonomy and Categorization
A jumbled list of skills is unreadable to a human and confusing to a machine. Grouping skills maximizes readability.
| Group | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Languages | For technical roles, defining coding capability. | Java, Python, C++, SQL. |
| Software & Tools | Defines the operational stack. | Salesforce, HubSpot, Adobe CC, MS Office. |
| Core Competencies | Broad professional skills (often soft/hard hybrids). | Project Management, Strategic Planning, Budgeting. |
| Certifications | Verifiable credentials. | PMP, CPA, AWS Certified Solutions Architect. |
The "Gap Analysis" Prompt
After tailoring the Experience section, use the Skills section to plug any remaining keyword holes.
Prompt: "Compare my current resume (attached) against the Job Description (attached). Identify any keywords from the JD that are missing from my resume. List them. Then, suggest a 'Technical Skills' section that includes these missing keywords (only if they are relevant to my actual experience).".
Warning on Honesty: The prompt includes the constraint "only if relevant." It is vital to instruct the AI not to invent skills. AI has a tendency to be a "people pleaser" and might add "Oracle Database" simply because the JD asks for it, even if the candidate never mentioned it.
The Formatting Paradox: Where AI Fails
This section addresses the most significant technical hurdle in using ChatGPT for resumes: the output format. While ChatGPT generates text, it does not generate files (in the traditional sense of a formatted Word doc). It outputs Markdown, code blocks, or raw text.
The "Table" Trap
Users frequently ask ChatGPT to "Format this in a table." ChatGPT obliges, creating a Markdown table. The user then copies and pastes this into Word.
- The Technical Failure: When an ATS parser encounters a table, it often strips the cell borders and reads the text linearly across the row. A layout that looks like:
| Date | Company | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Engineer |
*Reads as:* "Date Company Role Google Engineer."
This destroys the chronological logic of the resume, causing the parser to fail in identifying the work history.
The "Columns" Confusion
Similarly, users often ask for a "two-column layout" to save space.
- The Technical Failure: Older parsers (still used by many Fortune 500s) read strictly left-to-right. They do not recognize the column break.
Left Column: 2020-2022
Right Column: Skills: Java
Parser Read: "2020-2022 Skills: Java"
The skill "Java" becomes associated with the date, or the date becomes a skill. The data is corrupted.
The Solution: Plain Text to Template
To ensure ATS compliance, the workflow must be:
- Generate Content in ChatGPT: Ask for "Plain text, bulleted lists, standard headers."
- Strip Formatting: Copy the text into a simple text editor (Notepad) to remove hidden HTML or Markdown code.
- Paste into a Clean Template: Paste the text into a standard Microsoft Word (.docx) document that uses simple, single-column formatting.
- Save as PDF (Optional): Only save as PDF if the JD explicitly allows it; otherwise,.docx is the safest format for parsing.
Risk Analysis: Privacy, Hallucination, and Detection
The use of AI in recruitment is not without peril. Candidates must navigate ethical, security, and quality risks.
Data Privacy and PII Leakage
When a user types data into the free version of ChatGPT, that data may be used to train future models.
- The Risk: Inputting a resume with a home address, phone number, and current employer's confidential project details constitutes a security leak. There have been documented cases of "memory" features in LLMs retaining and surfacing PII.
- Corporate Espionage: pasting "Strategies for [Company Name] Q4 Launch" into a public chatbot is a violation of most corporate NDAs.
- Mitigation: Anonymize everything. Before pasting the Master Resume, replace the name with "Candidate," the company with "[Current Employer]," and remove all contact info.
The Hallucination Hazard
LLMs are probabilistic, not deterministic. They fill gaps with statistically likely text.
- The Risk: If a candidate has a gap in their employment, ChatGPT might invent a "Freelance Consultant" role to fill it. If the JD requires "Tableau," and the candidate mentions "data visualization," ChatGPT might explicitly write "Expert in Tableau" even if the candidate has never used it.
- The Consequence: This is fraud. If discovered during a background check or technical interview, it leads to immediate disqualification and potential blacklisting.
- Mitigation: The user must be the "Editor-in-Chief." Every single claim generated by the AI must be verified against the candidate's actual memory and experience.
The "AI-ese" Tone
Recruiters are becoming adept at spotting AI-written text. Markers include:
- Overuse of words like "spearheaded," "orchestrated," "comprehensive," "tapestry," and "landscape."
- Perfectly uniform sentence length.
- A lack of personal voice or nuance.
- The "Uncanny Valley": A resume that is grammatically perfect but emotionally hollow triggers a negative response in human readers.
- Mitigation: Use prompts that request specific tones: "Write in a direct, conversational, yet professional tone. Avoid buzzwords. Vary sentence structure.".
The Reztune Paradigm: The All-in-One Solution
The process described above - while effective - is arduous. It requires the candidate to be a prompt engineer, a data sanitizer, a copywriter, and a layout designer. It involves switching between browser tabs, text editors, and word processors. It carries the constant risk of formatting errors and privacy breaches.
This complexity creates the market need for a specialized solution. Reztune emerges not just as a tool, but as an integrated platform that automates the entire workflow while mitigating the risks associated with raw LLM usage.

Comparative Analysis: Reztune vs. Manual ChatGPT
The following analysis highlights why dedicated software architecture is superior to ad-hoc prompting for high-stakes career moves.
| Feature | ChatGPT (Manual Process) | Reztune (Automated Platform) |
|---|---|---|
| ATS Compliance | Zero. The user is 100% responsible for formatting. High risk of parsing errors with tables/columns. | Native. Templates are pre-engineered and tested against major ATS parsers (Taleo, Greenhouse) to guarantee readability. |
| Tailoring Workflow | Manual Loop. Copy JD -> Write Prompt -> Paste Resume -> Edit Output -> Format in Word. Time: 30-60 mins per app. | One-Click. Import Resume -> Paste JD -> Click "Tailor". The engine auto-optimizes keywords and bullets. Time: 2-5 mins. |
| Hallucination Control | High Risk. The LLM has free rein to invent facts to please the user. | Constrained Generation. Reztune's AI is grounded in the user's verified profile data, preventing the invention of fake skills. |
| Data Privacy | Public Training. Data often trains the public model (Free Tier). PII leakage risk. | Private Instance. Data is processed in a secure, isolated environment compliant with GDPR/CCPA standards. |
| Content Quality | Generic. Often produces robotic "AI-ese" unless heavily prompted. | Fine-Tuned. The model is specifically fine-tuned on successful resumes, not general internet text, ensuring a high-impact professional tone. |
The Reztune Advantage: Structural Integrity
Reztune solves the "Formatting Paradox" (Section 8) by decoupling content generation from content presentation.
- The Engine: The AI analyzes the JD and the user's profile to generate optimized text (bullet points, summaries) that achieves high semantic relevance.
- The Container: This text is dynamically injected into a rigid, ATS-proof template. The user does not need to worry about margins, fonts, or hidden tables. The system ensures the output PDF/DOCX is structurally perfect for parsing.
Real-Time Optimization Scoring
Unlike ChatGPT, which gives qualitative feedback ("This looks good"), Reztune provides a quantitative ATS Score. As the user edits the resume, the score updates in real-time, showing exactly how well the document matches the target JD. It highlights missing keywords and suggests specific insertions, effectively gamifying the optimization process and giving the candidate empirical confidence before they hit "Submit".
Conclusion
The era of the generic resume is over. In a market dominated by algorithmic filters, customization is the only viable strategy for survival. While ChatGPT offers a powerful linguistic engine for this purpose, it is a raw tool that requires significant expertise and time to wield safely. For the professional job seeker who values efficiency, security, and results, Reztune represents the next evolution of career technology - a dedicated architect that transforms the chaotic creativity of AI into a structured, compliant, and compelling career narrative.
By automating the tedious mechanics of tailoring and formatting, Reztune allows the candidate to focus on what truly matters: preparing for the interview and landing the job.